Pipetting Techniques
An explanation of forward and reverse pipetting techniques to get the highest quality data out of your TRPS system.
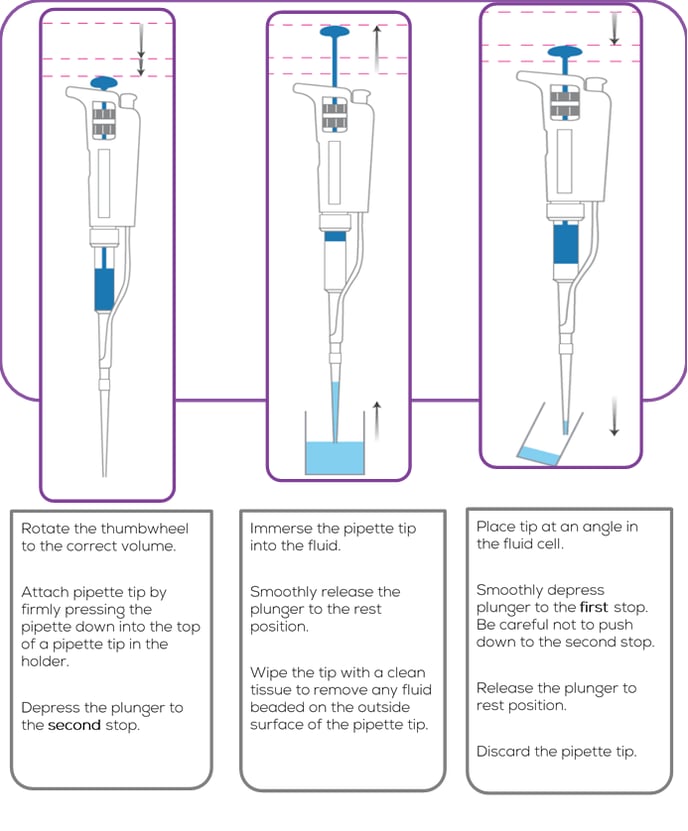
Forward Pipetting
Forward pipetting is the most commonly use pipetting technique, and most users will already be familiar with this. In the context of TRPS, this technique should be used for all particle dilution and dispensing.
Tips
- To reduce the error associated with your concentration results, always use calibrated pipettes.
- Always use the smallest pipette for the job e.g. use a 2 µL pipette for dispensing 1 µL rather than a 10 µL pipette, and use a 200 µL pipette for dispensing 150 µL rather than a 1000 µL pipette.
- Always wipe the outside of the pipette tip before dispensing, dispense the smaller volume into the larger volume, and pump the plunger 3-4 times before discarding the tip.
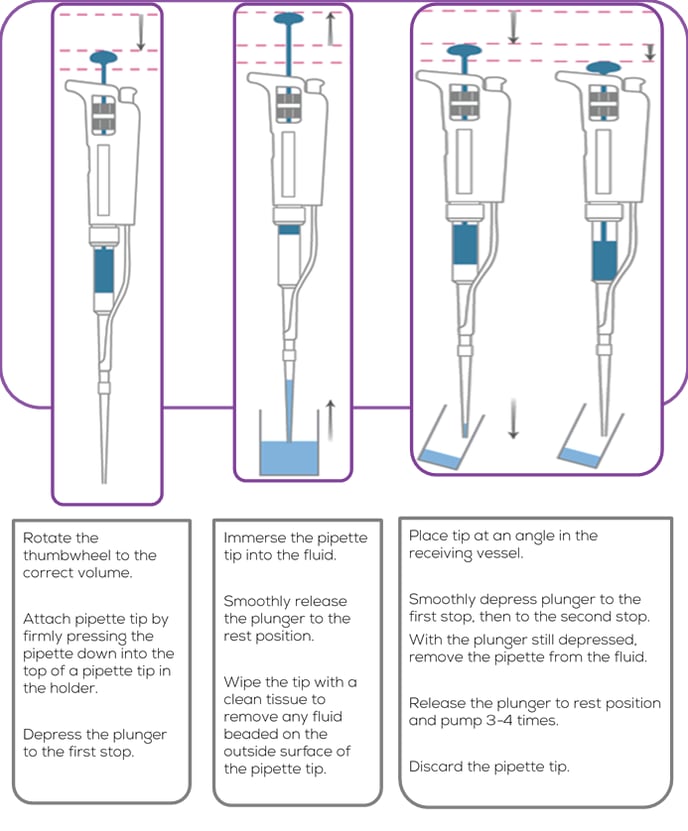
Reverse Pipetting
The most common cause of system instability is incorrect pipetting technique.
Using the standard forward pipetting technique for dispensing liquid into the fluid cells may introduce bubbles near the pore which can clog the pore and disrupt the baseline current and particle rate!
With reverse pipetting, you draw out more fluid than you dispense, minimising the risk of introducing bubbles into the fluid system. This technique should be used any time liquid is being introduced into the upper fluid cell.